Before 2002, Rose growers in Korea were worried to pay high royalty for the European Breeders.
However, after joining UPOV in 2002, Korean breeders have developed new registered varieties and
been promoting to export roses to various countries.
World Market and Korean variety roses

Korean variety roses occupy about 20% in the whole rose market in 2014, and its market share will be
getting increased for both domestic and overseas.
Let us show you some example of varieties.
“Feel Lip” is a deep purple rose and very highly-resistant variety for disease and pestilence.
It was not very common in domestic market, though, South America and Africa welcomed this variety
because of the characters such as shape, size and color.
The same as “Peach Valley” and “Pink Heart”.
These varieties were not so popular in national market due to their colors, but strongly supported in overseas market.
Main countries for export roses are South America and Africa.
Therefore, main markets for rose royalty business are these countries, too.
Especially farms in Kenya and Ethiopia are increasing in rose production.
Let me show you our update in South America and Africa.
South America
Ecuador
Cultivation environment:
Altitude 2,500~3,500m,
Temperature day24℃, night10℃
Strong sunlight, large temperature difference day and night
Rose is one of the main five exports of Ecuador.
Columbia
Cultivation environment:
Altitude 2,000m,
Temperature day22℃, night6℃
Strong sunlight, large temperature difference day and night
Almost export to USA, especially export of small quantity of high quality roses to Russia
Africa


Kenya
Cultivation environment:
Altitude 0~1,500m,
Temperature day26℃, night10℃
Water shortage in dry season, many venom insect
Strong sunlight, large temperature difference day and night
Almost export to Europe
Ethiopia
Cultivation environment:
Altitude 2,000~3,000m,
Temperature 16~22℃
Water shortage in dry season
Best weather for growing
Almost export to Europe
Cutting down for equipment cost
Rose growers in South America and Africa cultivate roses in plastic house not in glass house.
The equipment cost for plastic house is only 10% of one for glass house.
Sales Report of GARES
GARES, Korean rose breeding company, sold total 2,892,188 rose plants till year 2014 and breed 9
commercial varieties. 186 farms over 19 countries grow GARES varieties.
Becoming royalty receiver
Korean growers pay rose royalty abroad about 1,040,000 plants in 2014.
On the other hand GARES rose varieties are sold about nearly 3 million in year 2014.
It proves that Korea has changed from royalty payer to royalty receiver.

(Mr. Charlie Jeong, wonwoo trading, at KSVS
Symposium on Plant Variety Protection,
September 3, 2015)
Ashiro region of Hachimantai-shi, is in the northwest part of Iwate prefecture in Japan.
In 1970s people in this community started growing rindo, the Japanese word for gentian.
They developed their original varieties and registered them based on UPOV convention,
aiming to export gentian for expanding demand.
They finally succeeded in increasing the farmers’ benefit by enlarging the sales network all over the world.
Now about 170 farmers are growing “Ashiro Rindo”, their original varieties,
marketing them to New Zealand, Chili, Holland and other countries.
Development of original varieties
In late 1960s, people in Ashiro region found it difficult to support their family particularly in winter.
Many head of households went to Tokyo to work.
To gain income in hometown during the winter time, they decided gentian cultivation.
And then they started developing original varieties to avoid price competition in domestic gentian market.
To expand domestic demand, they developed new varieties which can be shipped for 4 months, from July to October.
Gentian cultivation in New Zealand and Chili and cut flower export
Their next strategy was to develop overseas gentian market.
They started cultivation Ashiro Rindo varieties in New Zealand in 1995.
The purpose of this is to import Ashiro Rindo cultivated in New Zealand to the Japanese market during the winter to keep up with demand.
They launched the same scheme to Chili afterward.
Their licensing business model for selling seedling, instruction of cultivation, export and receiving royalty in international market has been established.
They launched to export cut flowers of Ashiro Rindo from New Zealand and Chili.
The EU market imports them from New Zealand and US imports them from Chili.
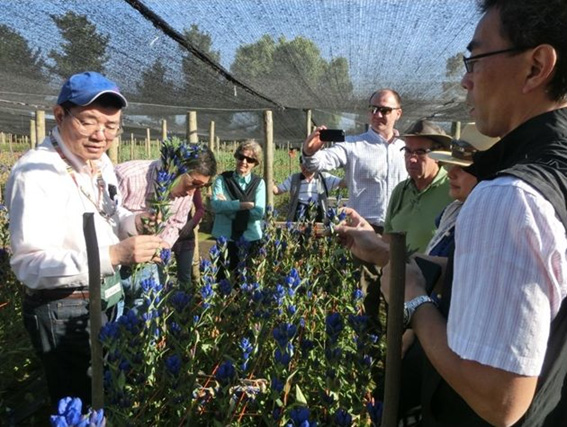

Ashiro Rindo cultivation in Chili
Export cut flowers to Holland and Branding Strategy
Farmers in Ashiro began exporting cut flowers of Ashiro Rindo to Holland in 2002.
Entering the Holland market, they struggled to compete domestic gentian which were cheaper than Ashiro Rindo.
They found needs of branding strategy.
Illustrated maps of Ashiro and stickers of Ashiro Rindo brand logo are placed on a bucket with the cut flowers for appealing its high quality and uniformity.
Ashiro Rindo varieties were registered in EU in 2005 and obtained a trademark registration in 2008.
Exports to Singapore, US., and Hong Kong from Japan have started since 2011.
In 2014, the export volume of Ashiro Rindo from Japan to EU was 67,000 stems and its sales surged at 37% over the previous year.

Ashiro Rindo sold in auction in Holland
With a view to global market, people involved Ashiro Rindo have been setting out to keep competitive advantages by selling Ashiro Rindo worldwide and investing the revenue to new variety development and fostering of human resources.